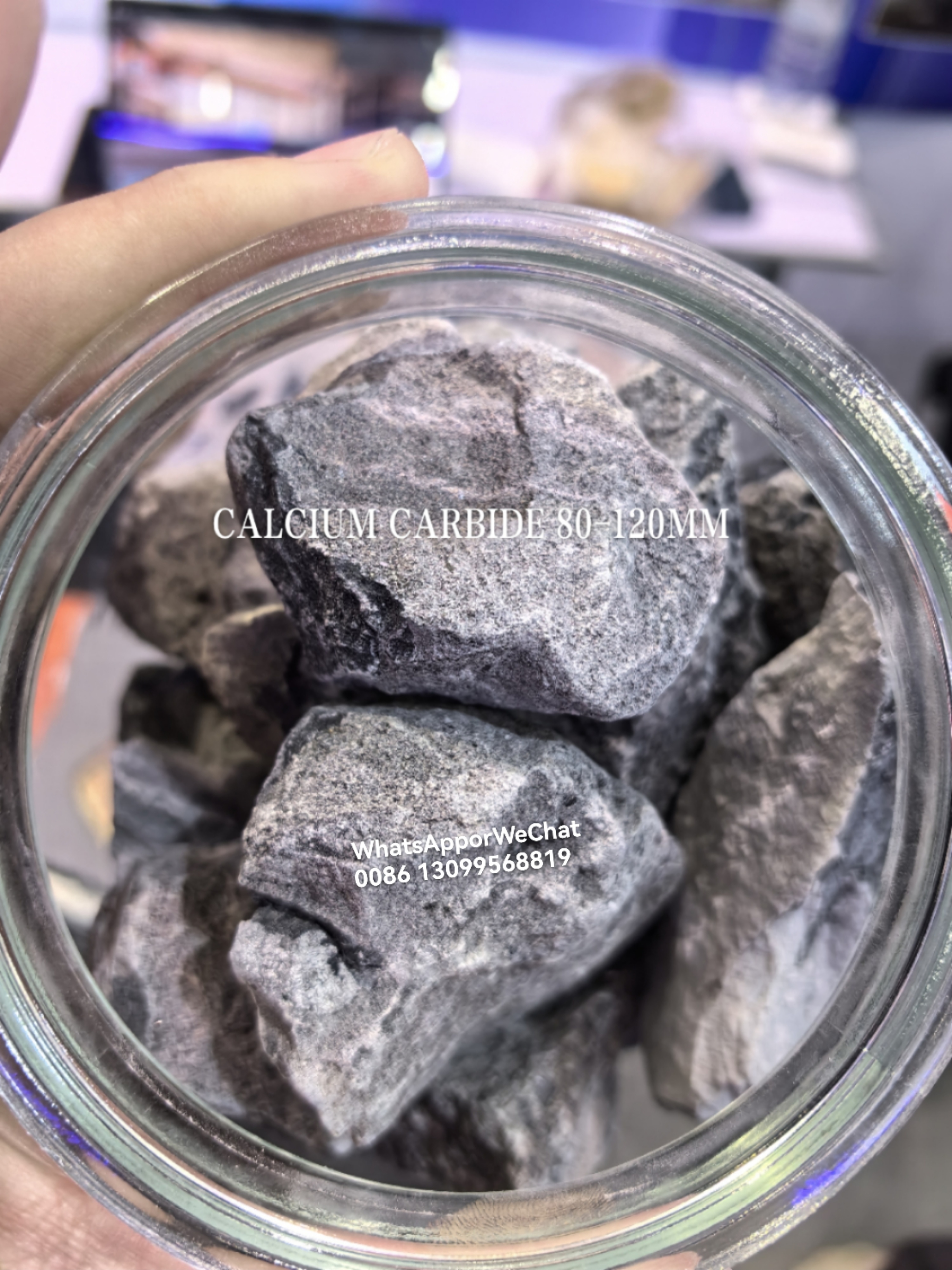
Calcium Carbide
Calcium carbide is the premier slag conditioner and desulfurizer for steel; it produces acetylene gas - a precursor to many specialty chemicals and an invaluable tool for construction; and it is critical for removing pollutants from the environment. The chemical energy provided by calcium carbide has fueled industrial innovation, making it an important raw material for a wide range of basic industrial needs.
In the production process, the raw materials lime and coke are mixed and heated to over 2000 degrees Celsius. The reaction is carried out in our low shaft furnace using an electric arc, which is very energy intensive.
In metallurgy, our customers value calcium carbide for its ability to treat alkaline slags and reduce dissolved metals. Acetylene produced in contact with water is favored for its very high welding temperatures. No other hydrocarbon can achieve such high localized welding temperatures.
Advantages of Calcium Carbide
-
High cost saving potential — reduces overall production costs by lowering energy consumption and minimizing the need for expensive deoxidizers, addressing challenges related to high production expenses and inefficient energy use.
-
Minimal and high sulfur content in slag — allows better control of slag composition, improving process stability and steel quality while preventing issues caused by inconsistent sulfur levels.
-
Recovery of chromium, manganese, silicon and iron from slag — enables effective resource recycling and minimizes the loss of valuable alloying elements, enhancing resource utilization and reducing raw material consumption.
-
Increased purity due to gaseous deoxidation products — ensures cleaner metal with fewer inclusions and more stable mechanical properties, solving common problems of impurity and inclusion formation in steelmaking.
Applications of calcium carbide
Desulphurization (direct)
In modern steelmaking operations, the demand for low-sulfur steels in modern continuous casting operations and special applications has increased the attractiveness of calcium carbide as a desulfurizer for molten iron.
Slag conditioning
Carbide is an important tool for removing unwanted iron oxides from the slag brought into the ladle during the steel out process. When the coarser carbide is added to the liquid metal stream or to the ladle after steel is discharged, it reacts with the oxides and recovers iron and expensive alloys that would otherwise be lost. In addition, if left untreated, these oxides can interfere with downstream steel refining operations by inhibiting desulfurization, oxidizing (“discoloring”) alloy additions, and eroding refractory materials.
Furnace Injection
Carbide has the unique ability to react only with metal oxides without adversely affecting the chemistry of the steel, thus adding significant energy to the process. In an electric arc furnace (EAF), the energy generated during oxide reduction is accompanied by the production of heated lime particles and CO gas, which helps to retain the heat generated while increasing the foaming capacity of the EAF slag.
In addition, since most of the slag produced in an EAF is not discharged into the ladle, all of the well-known advantages of oxide reduction and alloy recovery in ladle metallurgy can be utilized by the EAF on a larger scale.
The result is a more energy-efficient, faster and more productive electric arc furnace process with higher alloy recovery.
Chemical acetylene
Although calcium carbide can be used directly as a process material, its primary use and perhaps greatest versatility is realized when this rock-like substance reacts with water to form acetylene and calcium hydroxide. The unique chemistry of the three-bonded carbon in the acetylene molecule permits a variety of useful chemical reactions to form intermediates used in the manufacture of various chemical derivatives.
Cutting and Welding
Using a device called a generator, calcium carbide undergoes a controlled reaction with water to convert to acetylene. Acetylene (C2H2) is a very useful hydrocarbon because energy is locked up in the triple bond between two carbon atoms. This energy is then released and used in different ways by our customers for various industrial purposes.
Environmental Engineering
Calcium hydroxide is a by-product of the acetylene generation process and is very useful in various industrial applications. Probably the best-known use of our calcium hydroxide is for purifying flue gases produced by fossil fuel power plants to remove sulfur compounds and prevent them from being released into the air.
Calcium Carbide Manufacturer
Wanding produces very good quality calcium carbide with an average gas yield of 300 liters per kilogram of calcium carbide.
The product is packed in containers (various types) or in 100 kg drums. In order to make the best use of shipping space, 9 drums can be placed on a pallet, which can then be loaded onto a truck or sea container to save space. We also accept customized packaging.
Small Particle Calcium Carbide 80-120 MM
Calcium carbide is produced industrially in an electric arc furnace from a mixture of lime and coke at approximately 2,200 °C (3,990 °F).It is a chemical compound with the chemical formula of CaC2.Its main use industrially is in the production of acetylene, calcium cyanamide, steelmaking, carbide lamps.
Calcium carbide is produced industrially in an electric arc furnace from a mixture of lime and coke at approximately 2,200 °C (3,990 °F).It is a chemical compound with the chemical formula of CaC2.Its main use industrially is in the production of acetylene, calcium cyanamide, steelmaking, carbide lamps.
Calcium Carbide 25-50mm for Desulfurization
Calcium carbide is produced industrially in an electric arc furnace from a mixture of lime and coke at approximately 2,200 °C (3,990 °F).It is a chemical compound with the chemical formula of CaC2.Its main use industrially is in the production of acetylene, calcium cyanamide, steelmaking, carbide lamps.
Calcium carbide is produced industrially in an electric arc furnace from a mixture of lime and coke at approximately 2,200 °C (3,990 °F).It is a chemical compound with the chemical formula of CaC2.Its main use industrially is in the production of acetylene, calcium cyanamide, steelmaking, carbide lamps.
Calcium Carbide 7-15mm is widely used in various industrial processes, including nitrogen fixation in cyanamide production and sulfur removal in the steelmaking industry. This chemical compound appears as a gray to black solid and exhibits high reactivity with water.
Calcium Carbide Particles 2-7 MM
Calcium carbide is produced industrially in an electric arc furnace from a mixture of lime and coke at approximately 2,200 °C (3,990 °F).It is a chemical compound with the chemical formula of CaC2.Its main use industrially is in the production of acetylene, calcium cyanamide, steelmaking, carbide lamps.